The bird flu strain is so deadly that it was created
Emergence and spread of novel H5N8 and H5.4 clade 2.3.4.4 highly pathogenic avian influenza in 2020
Lewis, N. S. et al. Emergence and spread of novel H5N8, H5N5 and H5N1 clade 2.3.4.4 highly pathogenic avian influenza in 2020. I am an emigre. Microbes Infect. 10, 148–151 (2021).
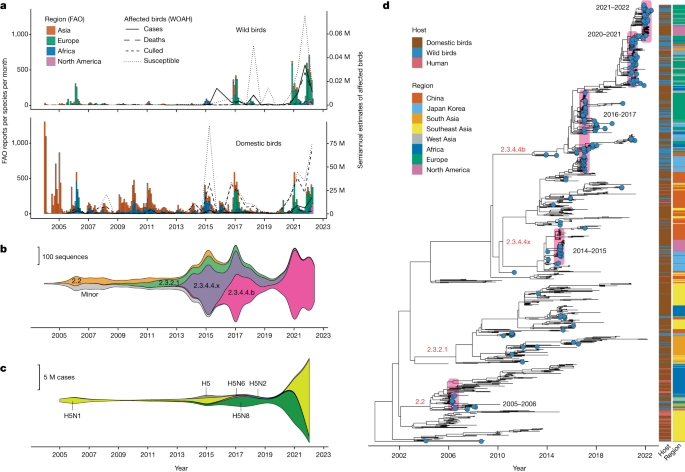
The study, published in Nature on 18 October1, looked at changes to the virus’s genome over time and used data on reported outbreaks to track how it spread.
Andy Ramey is a wildlife geneticist with the US Geological Survey Alaska Science Center, and he says that the pathogens used to be very obvious in poultry. The implications of that for both wildlife and humans are still being considered.
It developed two different types in the same year. One spread from northern Europe to North America by birds moving across the Atlantic Ocean. The other was taken around the Mediterranean Sea into Africa.
Influence of LPAI viruses on the evolution of H5N1: implications for the livestock sector and for the elimination of highly pathogenic avian influenza
Because of this, LPAI viruses — especially a strain called H9N2 — play a major part in the evolution of H5N1, he adds. They are not well monitored. “Eradication or elimination strategies that target these low pathogenic viruses would be a huge step forward in terms of controlling avian influenza itself,” says Dhanasekaran.
There may be two sides of the coin here. HPAI viruses can mutate through interactions with LPAI ones. In both, the genome is split into eight segments that can be mixed and matched. “When two viruses co-infect the same cell, they could swap their genes when the virus is getting packaged,” says Dhanasekaran.
Ramos, S., MacLachlan, M. & Melton, A. Impacts of the 2014-2015 Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Outbreak on the US Poultry Sector. The USDA has a livestock, dairy, and poultry outlook.
C. and Grund are members of the Association of American Publishers. Highly pathogenic avian influenza virus H5N1 from Egypt escapes vaccine-induced immunity but confers clinical protection against a heterologous clade 2.2.1 Egyptian isolate. Vaccine 29, 5567–5573 (2011).
J. et al. Influenza H5/H7 virus vaccination in poultry and reduction of zoonotic infections, Guangdong Province, China, 2017–18. It is an infectious disease called equig. Dis. 25, 116–118
Swieton, E. et al. Africa and Europe have a reassortant H5N8 virus. The person is known as the emigre. Infect. Dis. 26, 1557–1561, was published in 2020.
O G., Pybus and others. The emergence of emerging epidemics are being untangled. Proc. It was the Natl Acad. The USA’sSci. USA109, 15066/15 069 2012).
A. Kalkalauss, et al. Sampling bias and model choice in continuous phylogeography: getting lost on a random walk. PLoS Comput. The Biol. 17 was published in 2011.
The range changes of eastern birds in response to climate change were evaluated by Rushing and Royle. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 117, 12897–12903 (2020).
LABEL: a high-performance computer system for fast alignment assignment of influenza A hemagglutinins on smallholder poultry farms
Boni, M. F., Galvani, A. P., Wickelgren, A. L. & Malani, A. Economic epidemiology of avian influenza on smallholder poultry farms. Theor. There are 135 entries in the Biol. 90.
Shepard, S. S. et al. LABEL: fast and accurate lineage assignment with assessment of H5N1 and H9N2 influenza A hemagglutinins. PLoS ONE 9, e86921 (2014).
The tool for automated alignment trimming is called trimAl. Bioinformatics 25, 1972–1973 (2009).
Exploring the temporal structure of the sequence using TempEst. Virus Evol. 2, vew007 (2016).
Ayres, D. L. BEAGLE is a high- performance computing library and application programming interface. It’s the system of Syst. It’s a scientific journal. 61, 170–173 (2012).
Parker, J., Rambaut, A. & Pybus, O. G. Correlating viral phenotypes with phylogeny: accounting for phylogenetic uncertainty. Infect. The genes are Genet. Evol. 8, 239–246 (2008).
F. et al. The interactive visualization of the history of trait evolution. Mol. Biol. The Evol 33 contains a story titled “Nursing homes being built in England.”
The skyride through the rough skyline was made using coalescent-based inference of population dynamics. Mol. Biol. Evol. 25, 1459–1471 (2008).
Dellicour, S., Rose, R., Faria, N. R., Lemey, P. & Pybus, O. G. SERAPHIM: studying environmental rasters and phylogenetically informed movements. Bioinformatics 32, 3204–3206 (2016).

