A smart antibiotic can kill germs while sparing the environment
Lolamicin, a compound that selectively kills Gram-negative bacteria, and leads to susceptibility to Clostridium difficile-induced colitis
Gram-negative bacteria include public-health villains such as Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae. They cause diseases ranging from salmonella to cholera, and can trigger sepsis, a potentially lethal immune-system response to infection.
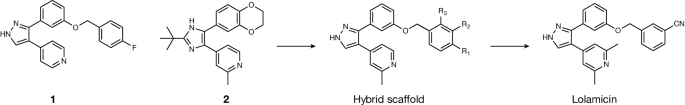
The study’s authors started with compounds that aren’t harmful to the bacterium but can affect theLol system, which is exclusive to Gram-negativebacteria. Tinkering with those compounds produced one that the researchers called lolamicin, which “selectively kills pathogenic bacteria over non-pathogenic bacteria based on differences in Lol proteins between these bacteria”, says study co-author Paul Hergenrother, a chemist at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
C. G. et al. were both authors of Buffie. Profound alterations of intestinal microbiota following a single dose of clindamycin results in sustained susceptibility to Clostridium difficile-induced colitis. Infect. Immun. 80, 62- 73.
Gitai says that the study “proves the viability” of targeting the Lol system, but adds, “There is a long road from showing efficacy in mice to developing a drug for human use.”
Gram-negative-selective antibiotic that spares the gut microbiome: Comment on a cautionary note on recent discoveries of fabimycin
Hiller makes a cautious note. He says there is not much money to be made with a novel antibiotic that has been approved for clinical use. “Around ten to twenty new Gram-negative antibiotics have been discovered in the last ten years”, he adds, but none has gained approval from the US Food and Drug Administration.
Lesniak, N. A., Schubert, A. M., Sinani, H. & Schloss, P. D. Clearance of Clostridioides difficile colonization is associated with antibiotic-specific bacterial changes. mSphere 6, e01238-20 (2021).
Parker, E. N. et al. The late-stage antibiotic candidate fabimycin, which is an antibiotic called FabI, was discovered through an iterative approach. ACS Cent. Sci. 8, 1145–1158 (2022).
McMurdie, P.J. and the rest of the team have created R package for interactive analysis and graphics of census data. A journal, pplone 8, e61217
Lan, Y., Wang, Q., Cole, J. R. & Rosen, G. L. Using the RDP classifier to predict taxonomic novelty and reduce the search space for finding novel organisms. PLoS ONE 7, e 32491 was published.
Source: A Gram-negative-selective antibiotic that spares the gut microbiome
Molecular-dynamics simulation of lipids: CHARMM’s additive force field update and the toolkit for efficient lipid shuffling
Feller, S. E., Zhang, Y. H., Pastor, R. W. & Brooks, B. R. Constant-pressure molecular-dynamics simulation—the Langevin piston method. J. Chem. Phys. 103 was published in 1995.
The integration of the equations of motion of a system with constraints is studied. J. Comput. In 1975, Phys. 23, 327–341 was published.
Klauda, J. B. et al. The CHARMM’s all-atom additive force field for lipids has been updated. J. Phys. Chem. B 114 was written in 2010; read here.
Hart, K. et al. The treatment of the BI/biI equilibrium was improved as a consequence of the Optimization of the CHARMM Additive force field. J. Chem. Theor. Comput. 8, 348–362 (2012).
Trott, O. & Olson, A. J. AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 31, 455–461 (2010).
The toolkit for efficient shuffling of the lipids in the biological membranes was developed by Licari, Dehghani-Ghahnaviran, S. and Tajkhorshid. There is a J. Chem. Inform. Model. 62, 986–996 (2022).
Source: A Gram-negative-selective antibiotic that spares the gut microbiome
Cell wall reporter assay for Gram-negative pathogens: A novel approach to countering resistance in E. coli by disrupting the outer portion of the cell
J. D., Impey, R.W., and Klein were interested in comparing simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J. Chem. Phys. 79, 926–935 (1983).
Pandit, K. R. & Klauda, J. B. Membrane models of E. coli containing cyclic moieties in the aliphatic lipid chain. Biochim. A biophysy. The manuscript was filed in the years 1898, 1205–1216.
Rana, P. et al. FabI (enoyl acyl carrier protein reductase)—a potential broad spectrum therapeutic target and its inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. In 2020 Chem. 208, 112757.
Countering Gram-negative antibiotic resistance can be accomplished through disrupting the outer portion of the cell. Antibiotics 8, 163 (2019).
K.P., Purnapatre, and other members of the research team work on a project. In vitro and in vivo activities of DS86760016, a novel leucyl-tRNA synthetase inhibitor for Gram-negative pathogens. Antimicrob. 62 agents Chemother was released on July 17th.
C. Oefner is the author of an article. Increased interactions of iclaprim with the Staphylococcus aureus dihydrofolate reductase are what is responsible for the increase in affinity. J. Antimicrob. Chemother, oldid. 63, oldid.
M.Garcia Chavez, and others. Synthesis of fusidic acid derivatives yields a potent antibiotic with an improved resistance profile. The infections have been named by the American Society of Civil Surgeons as ACS Infect. Dis. 7, 493–500.
Nayar, A. S. et al. Novel antibacterial targets and compounds revealed by a high-throughput cell wall reporter assay. J. Bacteriol. 197, 1726–1734 (2015).
Richter, M. F. & Hergenrother, P. J. The challenge of converting Gram-positive-only compounds into broad-spectrum antibiotics. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 1435, 18–38 (2019).
Source: A Gram-negative-selective antibiotic that spares the gut microbiome
R. Pathania and his co-authors identify an inhibitors of bacterial lipoprotein targeting in Escherichia coli
The essential trafficking pathway for outer lipoproteins has been redefined. It was Proc. The National Acad. is the Natl Acad. Sci. USA 114, 4769–4774 (2017).
R. Pathania and his co-authors write a book called “Pathania, R. et al.” There is an inhibitors of bacterial lipoprotein targeting identified in Escherichia coli. There is Nat. Chem. The Biol. 5, 749–856 was published in 2009.
H.H. et al. The components of the machineries is dependent on the outer membrane’s targeting of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa proteins. mBio 2, e00246–00211 (2011).
Source: A Gram-negative-selective antibiotic that spares the gut microbiome
Studies of the interaction of thiourea compounds with a lipoprotein targeting chaperone in the gut microbiota: repertoire and variations
Barker, C. A. et al. Modification and studies of the interaction of thiourea compounds with a lipoprotein targeting chaperone. Med. Chem. It was Lett. 23, 2426–2431.
Falagas and Kasiakou discussed the revival of polymyxins as a management tool of multidrug-resistant infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 40, 1333–1341 was published in 2005.
Lagier, J. C., Million, M., Hugon, P., Armougom, F. & Raoult, D. Human gut microbiota: repertoire and variations. There is a front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2, 136 (2012).
The long-term persistence of resistant Bacteroides spp. and resistance genes were studied. Antimicrob. The Chemother was published in 2006
