Chandrayaan is at the high latitude of the moon
Chandrayaan-3: The 1992 Conference on Lunar and Planetary Instability, Volatility and the Regolith Composition
Snyder, G. A., Taylor, L. A., Liu, Y. G. & Schmitt, R. A. in Proc. 22nd The lunar and planetary institute had a conference in 1992.
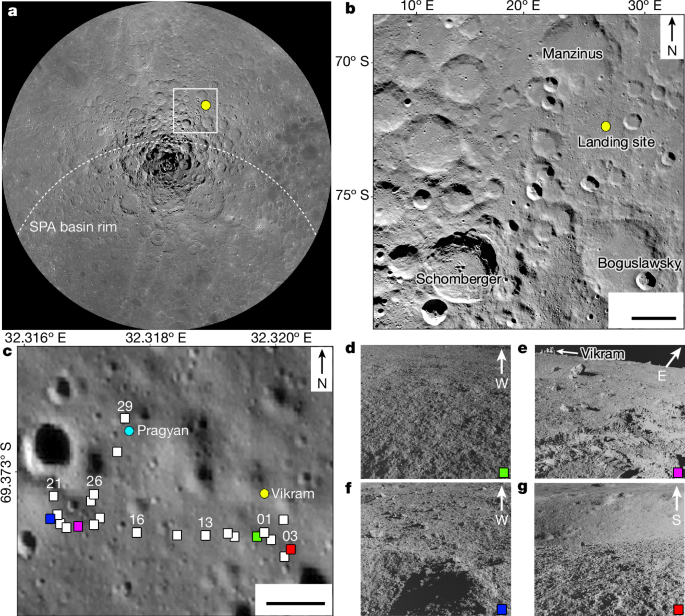
Chandrayaan-3’s Vikram lander touched down on 23 August 2023. It released a rover called Pragyan, which collected data ranging from temperature to seismological measurements over 10 days.
Pragyan also studied the chemical composition of the regolith: the fine material that covers much of the lunar surface. The rover stopped 23 times and deployed an instrument called an alpha-particle X-ray spectrometer (APXS).
“It’s sort of what we expected to be there based on orbital data, but the ground truth is always really good to get,” says Lindy Elkins-Tanton, a planetary scientist at Arizona State University in Tempe.
Anisotropy of the lunar basins revealed by Clementine laser ottimetry: Implications for Moon formation and the origin of the Moon
The best model for the origin of the Moon is that the newly formed Earth was struck by a large impactor called Theia, which blasted a large amount of material into the air. The moon was formed quickly by the scattered material. This impact theory explains why lunar rocks have an isotope composition similar to those on Earth.
Vadawale and his colleagues found that their samples contained elevated levels of magnesium compared with those of calcium. This suggests that deeper mafic material has been mixed into the regolith.
But one problem with that idea is that the South Pole–Aitken basin seems to be dominated by a mineral called pyroxene, which doesn’t quite fit Pragyan’s data, says Anand. Resolving this will probably require samples to be brought back to Earth, he says.
McGetchin, T.R., Settle, M., and Head have related implications for lunar basin deposits. Earth is a planet. Sci. Lett. 20, 226–236 (1973).
The maps of the lunar polar regions were created by using the data from the Kaguya profiler and laser ottimetry. Planet. Sci. 3, 63 was published in the year.
Spudis, P. D., Reisse, R. A. & Gillis, J. J. Ancient multiring basins on the Moon revealed by Clementine laser altimetry. Science 266, 1848–1851 (1994).
Calibration of Chandrayaan-2 Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer on-board. The case of N.P. and Mithun
The case of N.P. S. andmithun. A calibration of the Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer on-board Chandrayaan-2 was conducted using an empirical approach. Planet. The space sci book will be published in 2020.
There are hypotheses about the importance of FeO in the parent magma. Am. Mineral. 75, 46–58 (1990).
Cross,W., Iddings, J. P., and Washington are related to each other. A quantitative chemico-mineralogical classification and nomenclature of igneous rocks. J. Geol 10 was published in 1899.
Dygert, N., Lin, J.-F., Marshall, E. W., Kono, Y. & Gardner, J. E. A low viscosity lunar magma ocean forms a stratified anorthitic flotation crust with mafic poor and rich units. Geophys. Res. Lett. 44, 11,2,800–11,289.
There is a large amount of ejected objects from the Orientale Basin. Geophys. Res. Lett. 38, L17201 (2011).
Source: Chandrayaan-3 APXS elemental abundance measurements at lunar high latitude
Global Mapping of lunar refractory elements: multivariate regression vs. machine learning. The Chandrayaan-2 Large Area Soft X-ray Spectrometer (CLASS)
Arnaud, K. A., George, I. M. & Tennant, A. F. The OGIP spectral file format. https://heasarc.gsfc.nasa.gov/docs/heasarc/ofwg/docs/spectra/ogip_92_007.pdf (2021).
Bhatt, M., Wöhler, C., Grumpe, A., Hasebe, N. & Naito, M. Global mapping of lunar refractory elements: multivariate regression vs. machine learning. Astron. Astrophys 627 and A 155 were published in 2019.
N. S., Pillai, and others collaborated on the project. First results and in-flight performance of the Chandrayaan-2 Large Area Soft X-ray Spectrometer (CLASS). There are two works, Icarus 363 and 114436.
Source: Chandrayaan-3 APXS elemental abundance measurements at lunar high latitude
NORM4 spreadsheet programs to calculate petrologic norms from whole-rock chemical analyses. Biological and thermal histories of clasts in breccia 62224
Warren, P. H. et al. Seventh Foray: Whitlockite-rich lithologies, a diopside-bearing troctolitic anorthosite, ferroan anorthosites, and KREEP. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 88, B151–B164 (1983).
James, B. & Flohr went to work on the Mg-suite noritic rocks. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 88, A603–A614 was published in 1983.
The comparative thermal and mechanical histories of clasts in breccia 62224 were written by G. L. Jr and M. V. J. geography. Res. Solid Earth 88, A645–A657 (1983).
Hollocher, K. NORM4 Excel spreadsheet programs to calculate petrologic norms from whole-rock chemical analyses. Zenodo https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5818037 (2022).

